
In its form, as well as its size, are allowed.
Used to control the form, orientation, and cylindricity of a diameter relative to one or more datum axis. Used to control the form, orientation, and circularity of individual circular elements of a part feature relative to one or more datum axis.
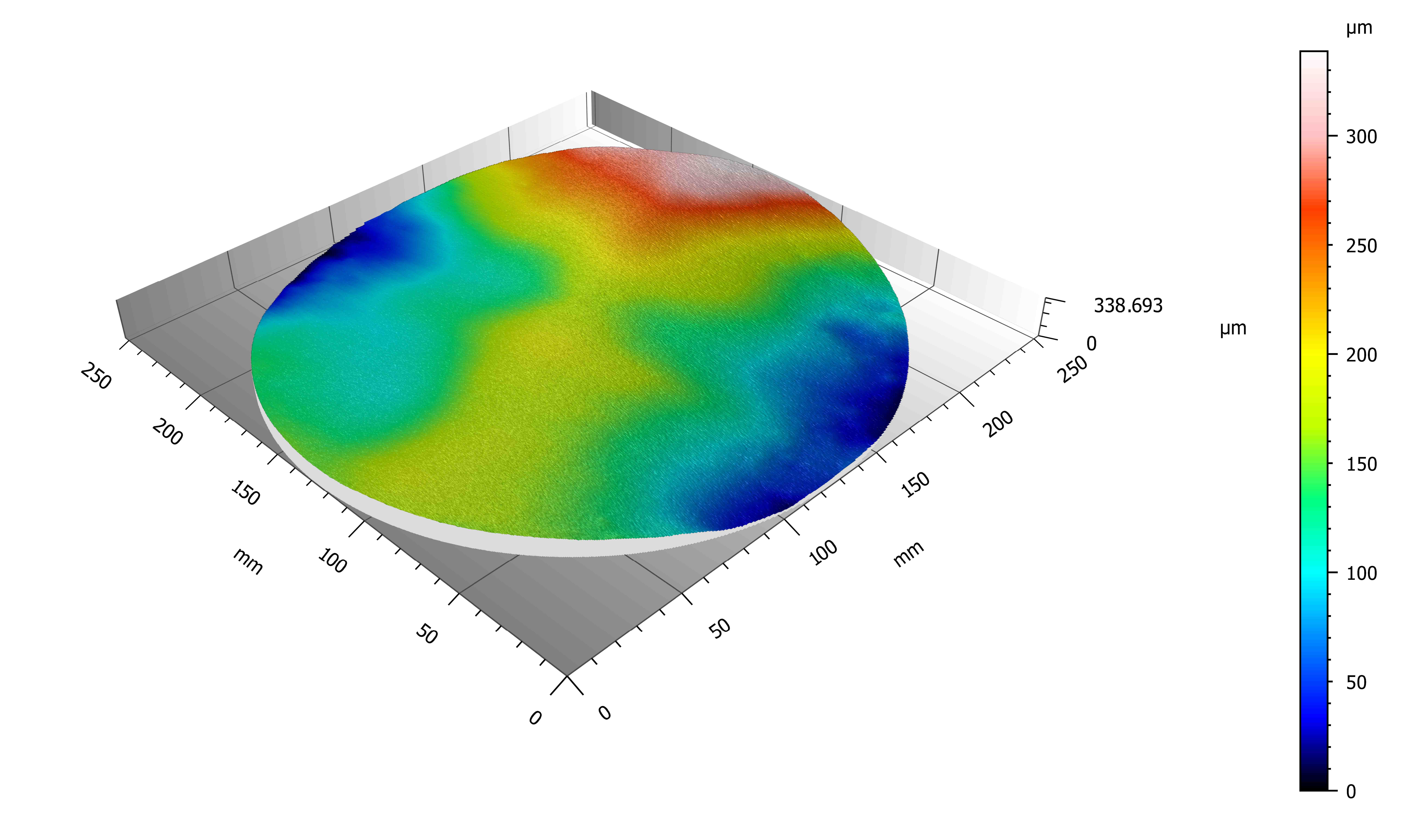
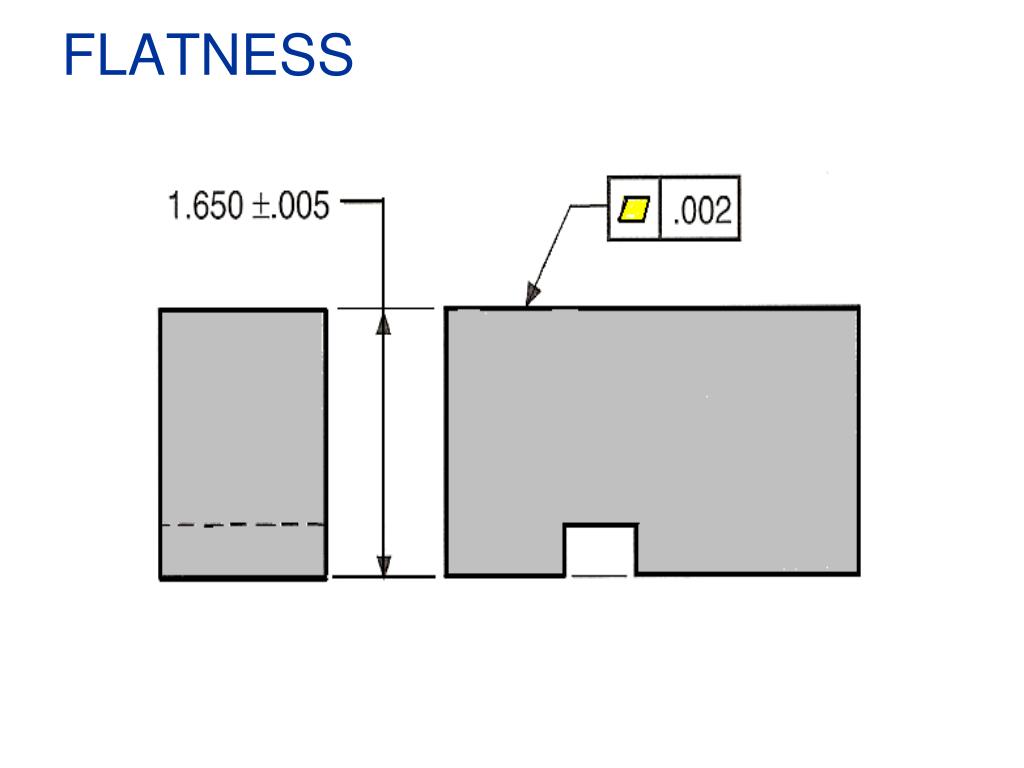
Used on planar FOS to ensure balanced distribution of mass and consistent wall thickness. Used on rotational parts to ensure balanced distribution of mass and consistent wall thickness. With respect to true position (theoretically exact location). Tolerance of position (TOP) is used to define the variation of location of a feature of size (FOS) Used to limit the amount a surface, axis, or centerplane is permitted to vary from being parallel to the datum. Used to control the amount a surface, axis, or centerplane is permitted to vary from 90° to the Datum. Used to control the amount a surface, axis, or centerplane is permitted to vary from its specified angle. Surfaces of revolution, or cones and coplanar surfaces. Used to control the size, location, orientation and form of planar, curved, or irregular surfaces, polygons, cylinders Used to limit the amount of error for line elements relative to their true profile. Used to limit the surface conditions (out of round, taper, and straightness) of a shaft diameter. Used to limit the lobing (out of round) of a shaft diameter, which can cause bearing or bushing failure. Used to control flatness for a gasket or seal, to attach a mating part or for better contact with a datum simulation surface.Īpplies without regard for the size of the feature (RFS).
Straightness tolerance specifies a tolerance zone within which the line element of a feature must lie. (click the control name for more details) GD&T Guide Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
